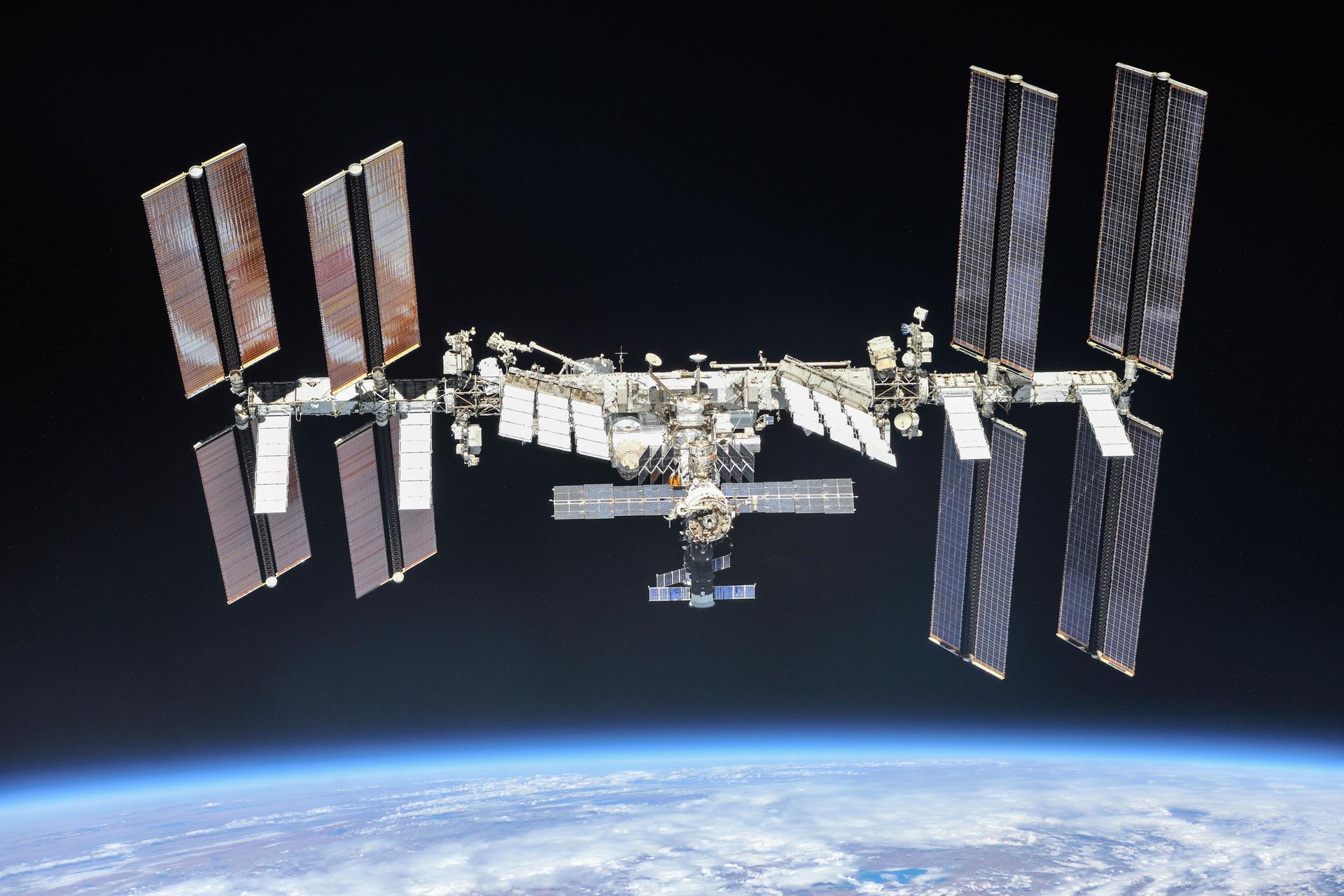
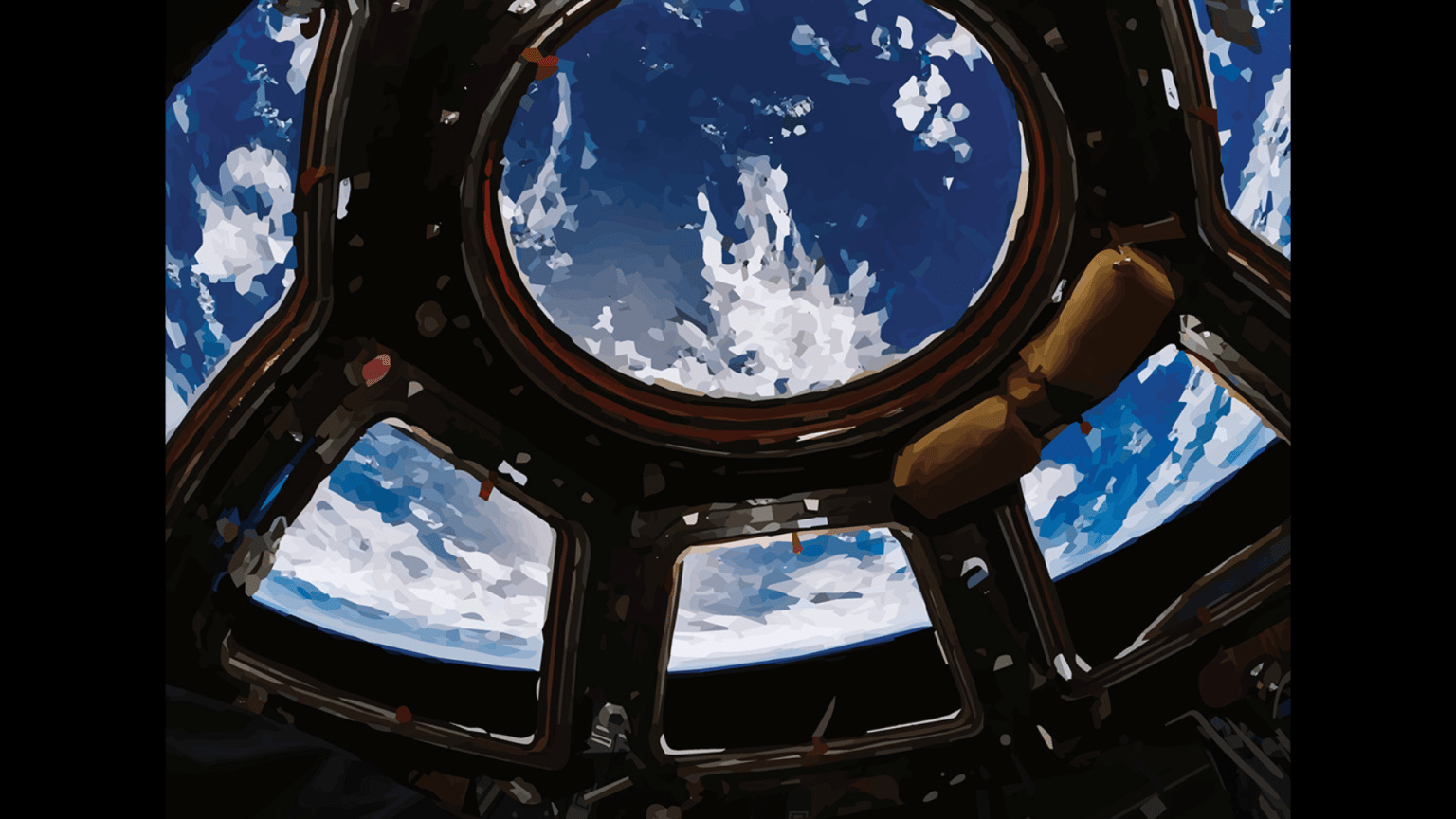
For more than 24 years, NASA has supported a continuous U.S. human presence aboard the International Space Station, advancing scientific knowledge and making research breakthroughs not possible on Earth for the benefit of humanity. The space station is a springboard to NASA’s next great leaps in exploration, including future missions to the Moon under Artemis, and ultimately, human exploration of Mars.
Read more about the groundbreaking work conducted in 2024 aboard the station:
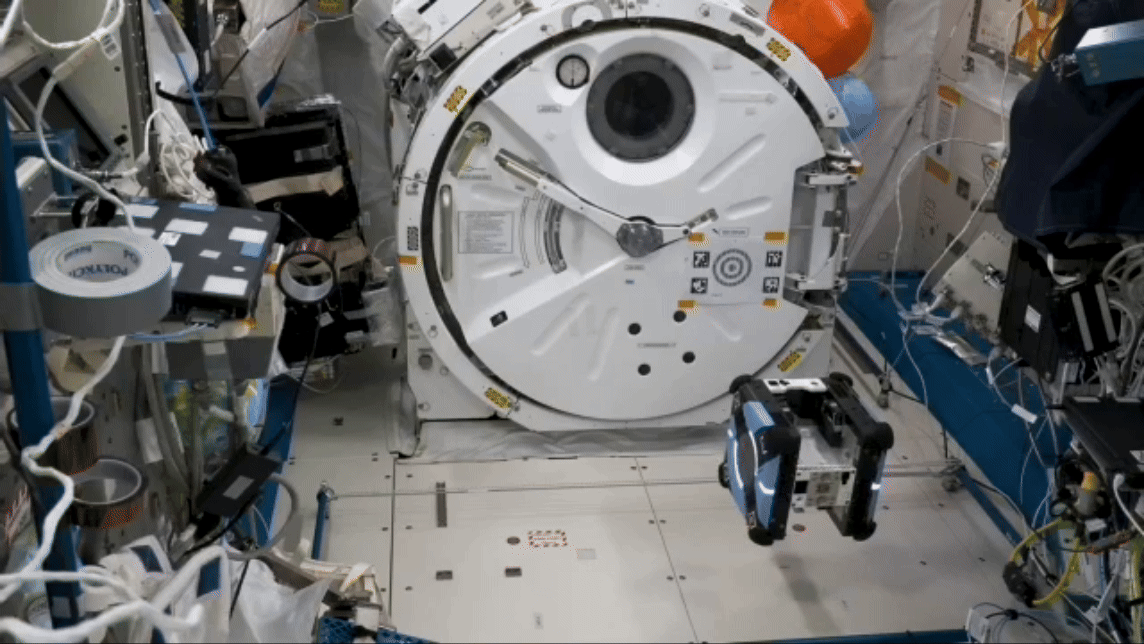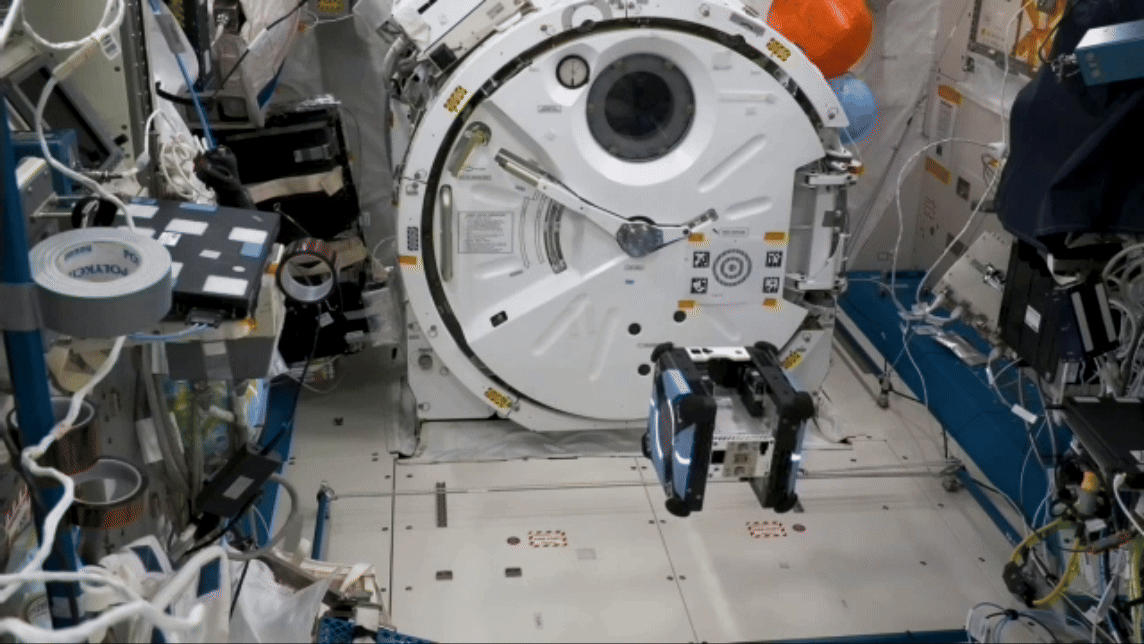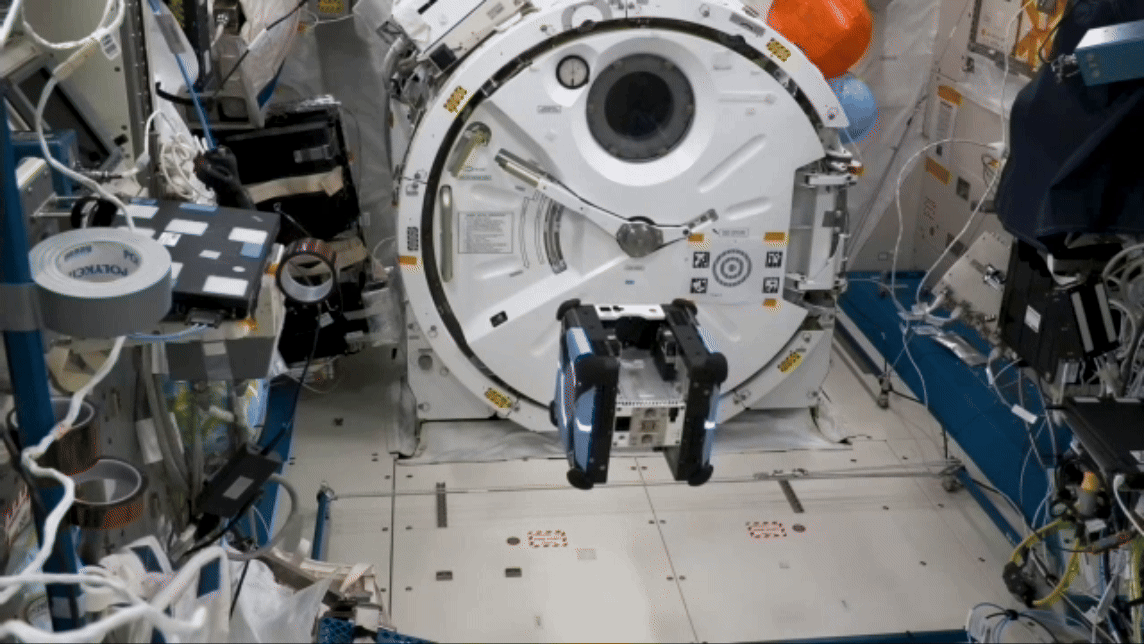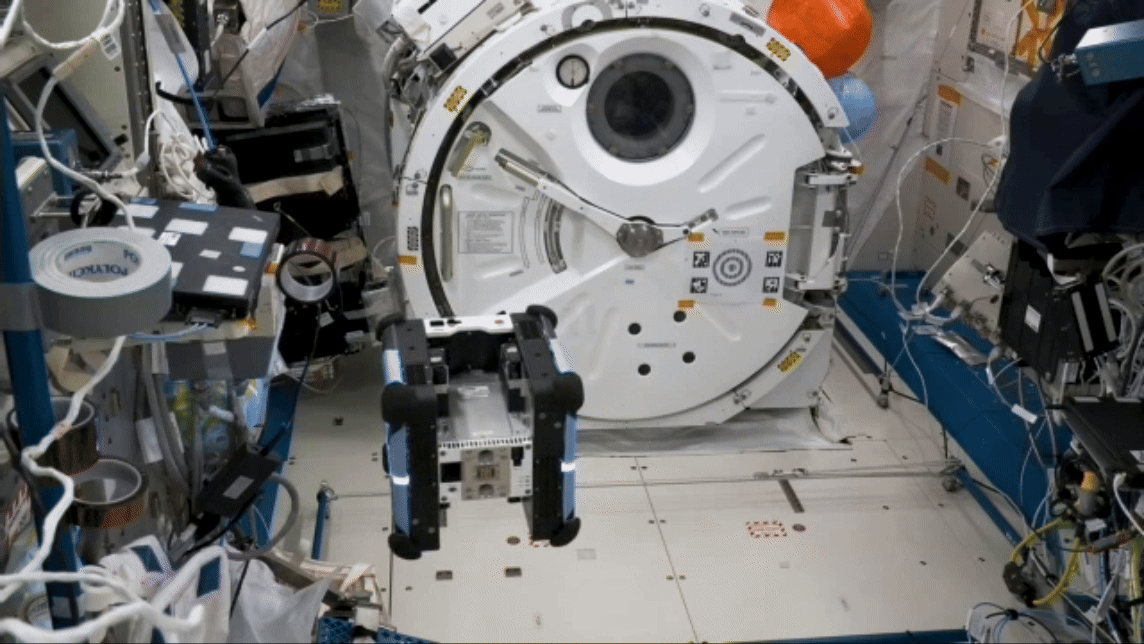
Robot performs remote simulated surgery
On long-duration missions, crew members may need surgical procedures, whether simple stitches or an emergency appendectomy. A small robot successfully performed simulated surgical procedures on the space station in early February 2024 for the Robotic Surgery Tech Demo, using two “hands” to grasp and cut rubber bands simulating tissue. Researchers compare the procedures conducted aboard the station and on Earth to evaluate the effects of microgravity and communication delays between space and ground.
3D metal print in space
On May 30,2024, the ESA (European Space Agency) Metal 3D Printer investigation created a small stainless steel s-curve, the first metal 3D print in space. Crew members on future missions could print metal parts for equipment maintenance, eliminating the need to pack spare parts and tools at launch. This technology also has the potential to improve additive manufacturing on Earth.
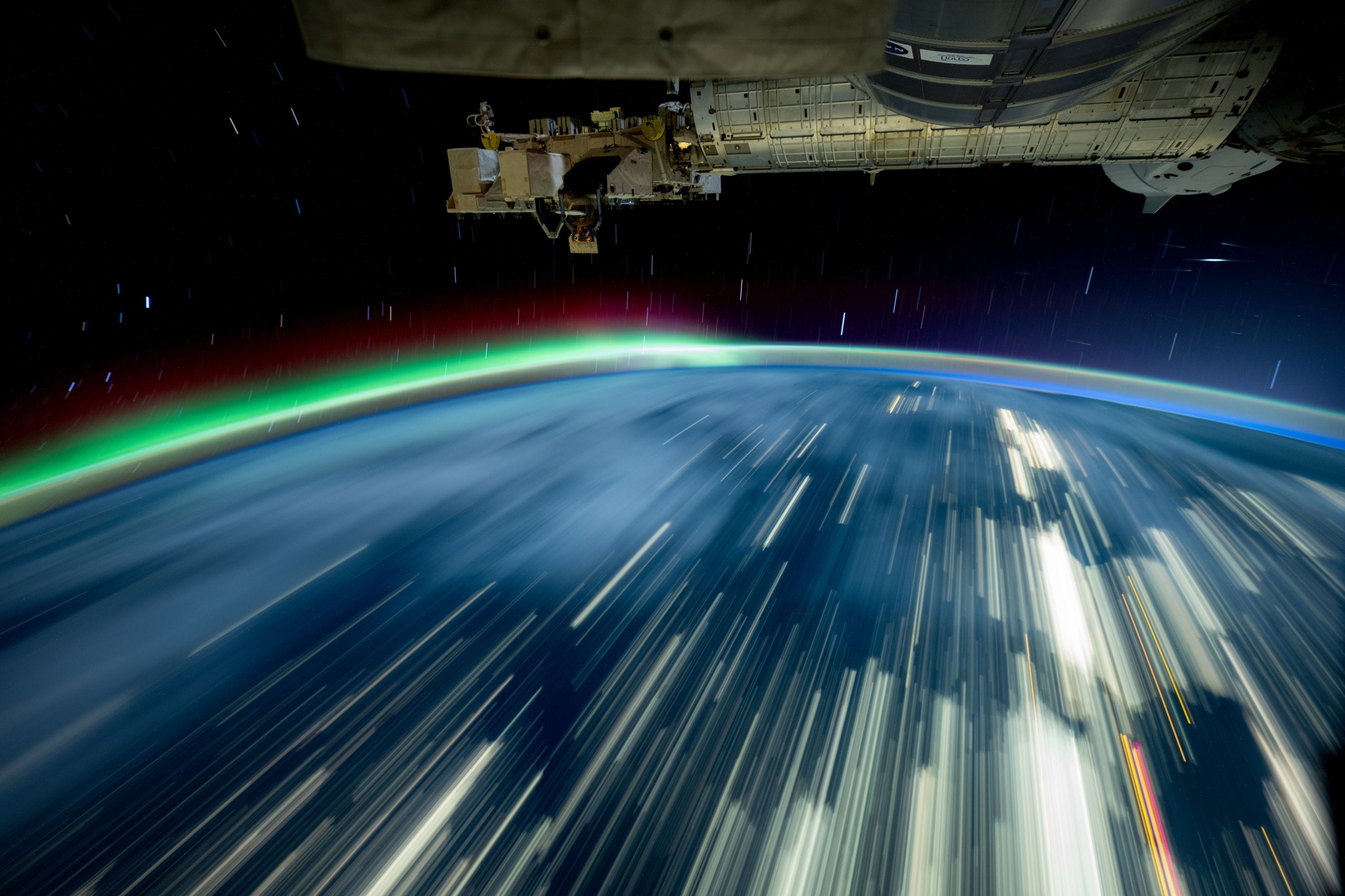
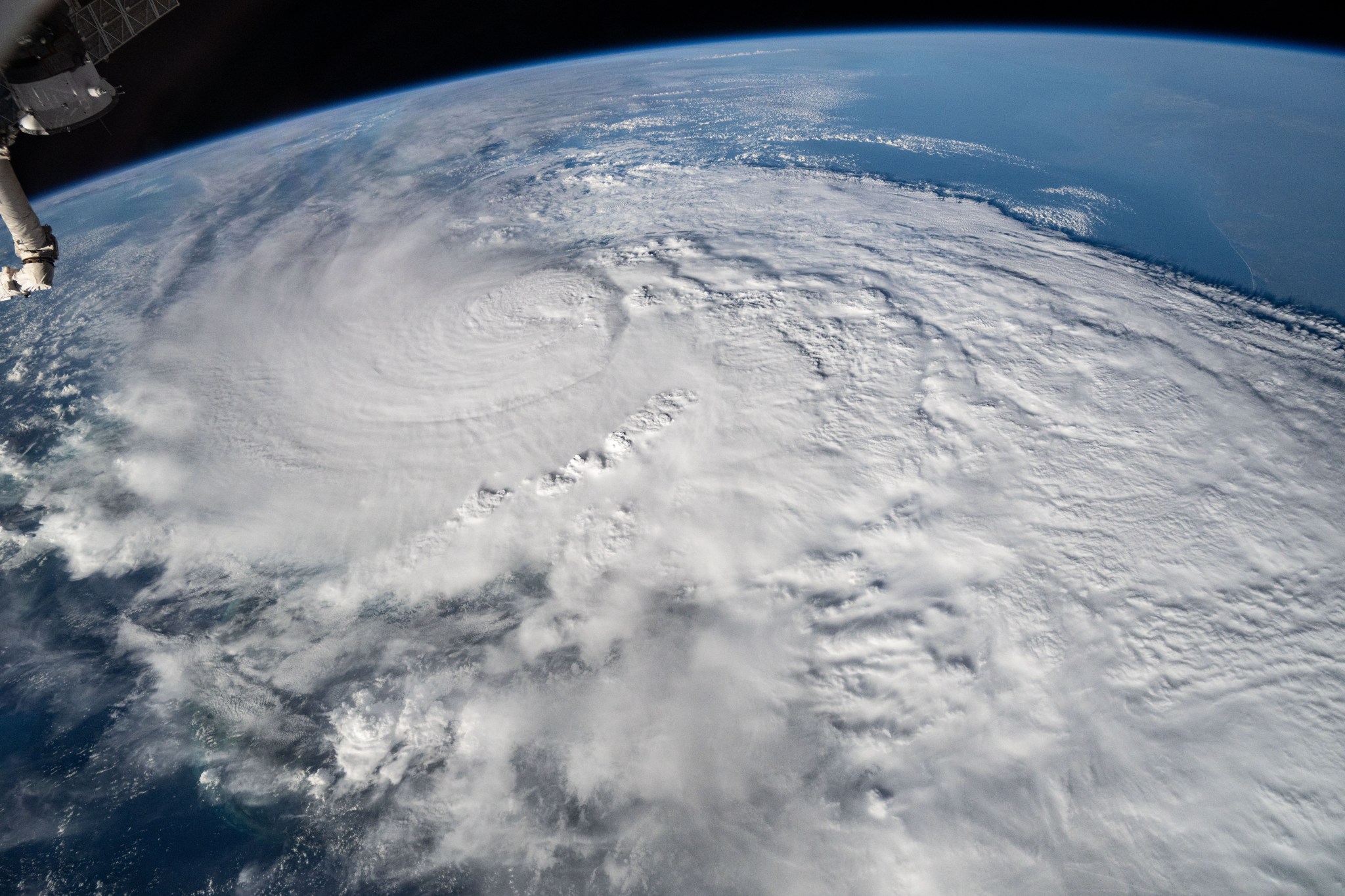
Here’s looking at you, Earth
The space station orbits roughly 250 miles above and passes over 90 percent of Earth’s population, providing a unique perspective for photographing the planet. Astronauts have taken more than 5.3 million images of Earth to monitor the planet’s changing landscape. The Expedition 71 crew took over 630,000 images, well above the average of roughly 105,000 for a single mission. This year, images included the April solar eclipse and auroras produced as the Sun’s 11-year activity cycle peaks. Others supported response to over 14 disaster events including hurricanes. In addition, 80,000 images were geolocated using machine learning, improving public search capabilities.
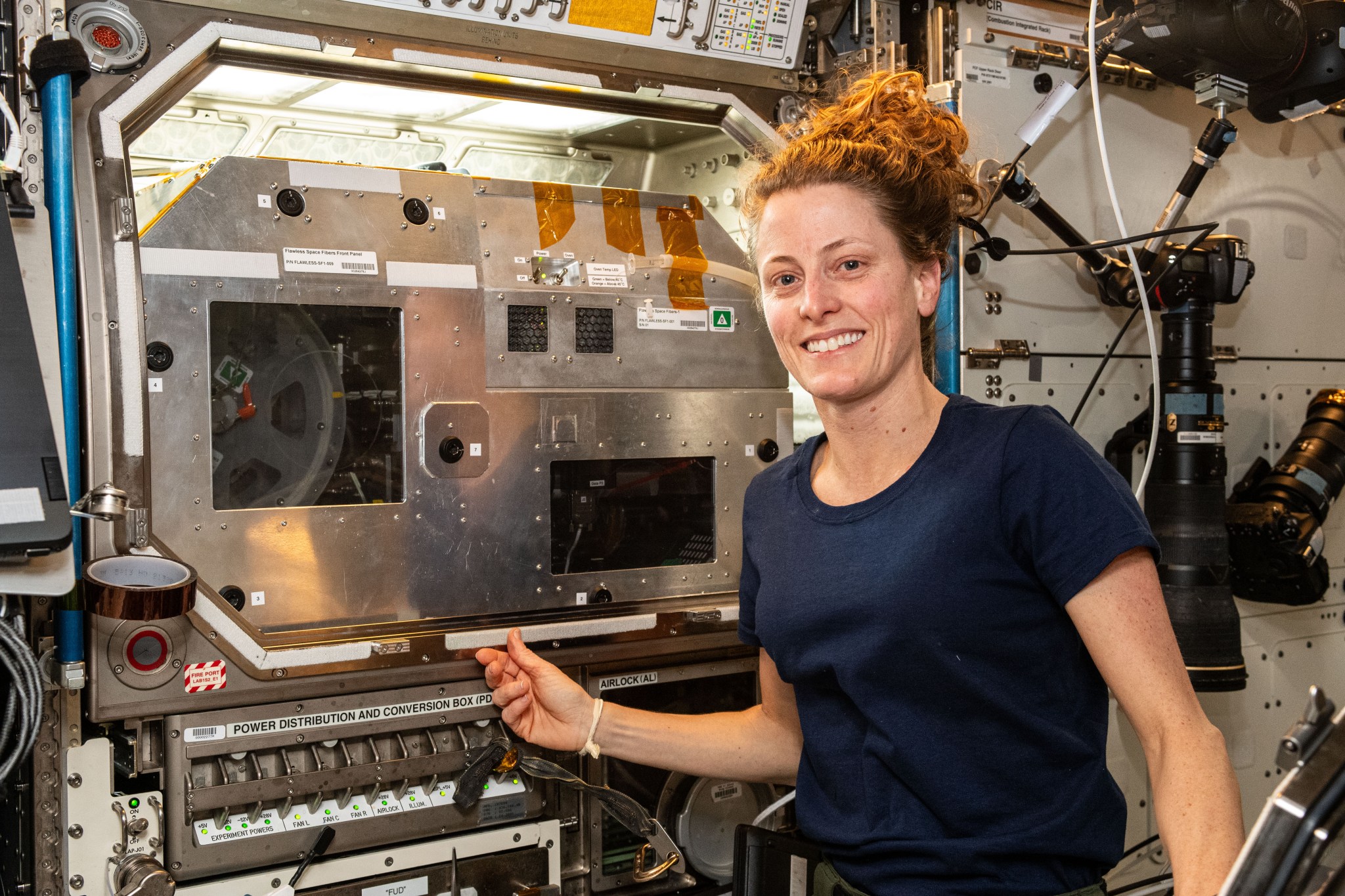
Miles of flawless fibers
From mid-February to mid-March of 2024, the Flawless Space Fibers-1 system produced more than seven miles of optical fiber in space. One draw of more than a half mile of fiber surpassed the prior record of 82 feet for the longest fiber manufactured in space, demonstrating that commercial lengths of fiber can be produced in orbit. Fibers produced in microgravity can be superior to those produced in Earth’s gravity. These fibers are made from ZBLAN, a glass alloy with the potential to provide more than 10 times the transmission capacity of traditional silica-based fibers.
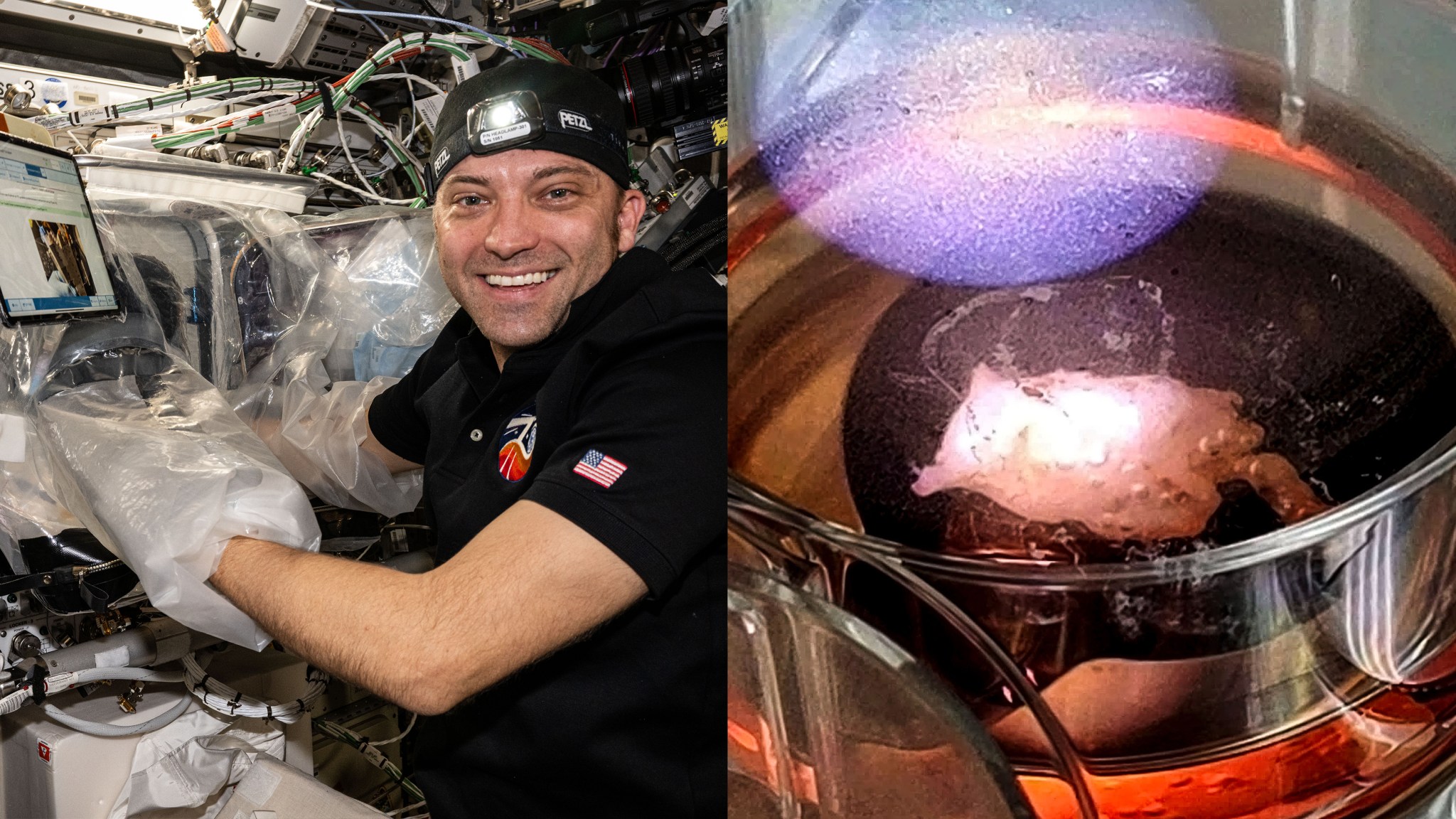
Tell-tale heart
In May 2024, BFF-Cardiac successfully bioprinted a three-dimensional human heart tissue sample using the Redwire BioFabrication Facility. Tissues bioprinted in the microgravity of the space station hold their shape without the use of artificial scaffolds. These bioprinted human heart tissues eventually could be used to create personalized patches for tissue damaged by events such as heart attacks. The tissue sample is undergoing further testing on Earth.
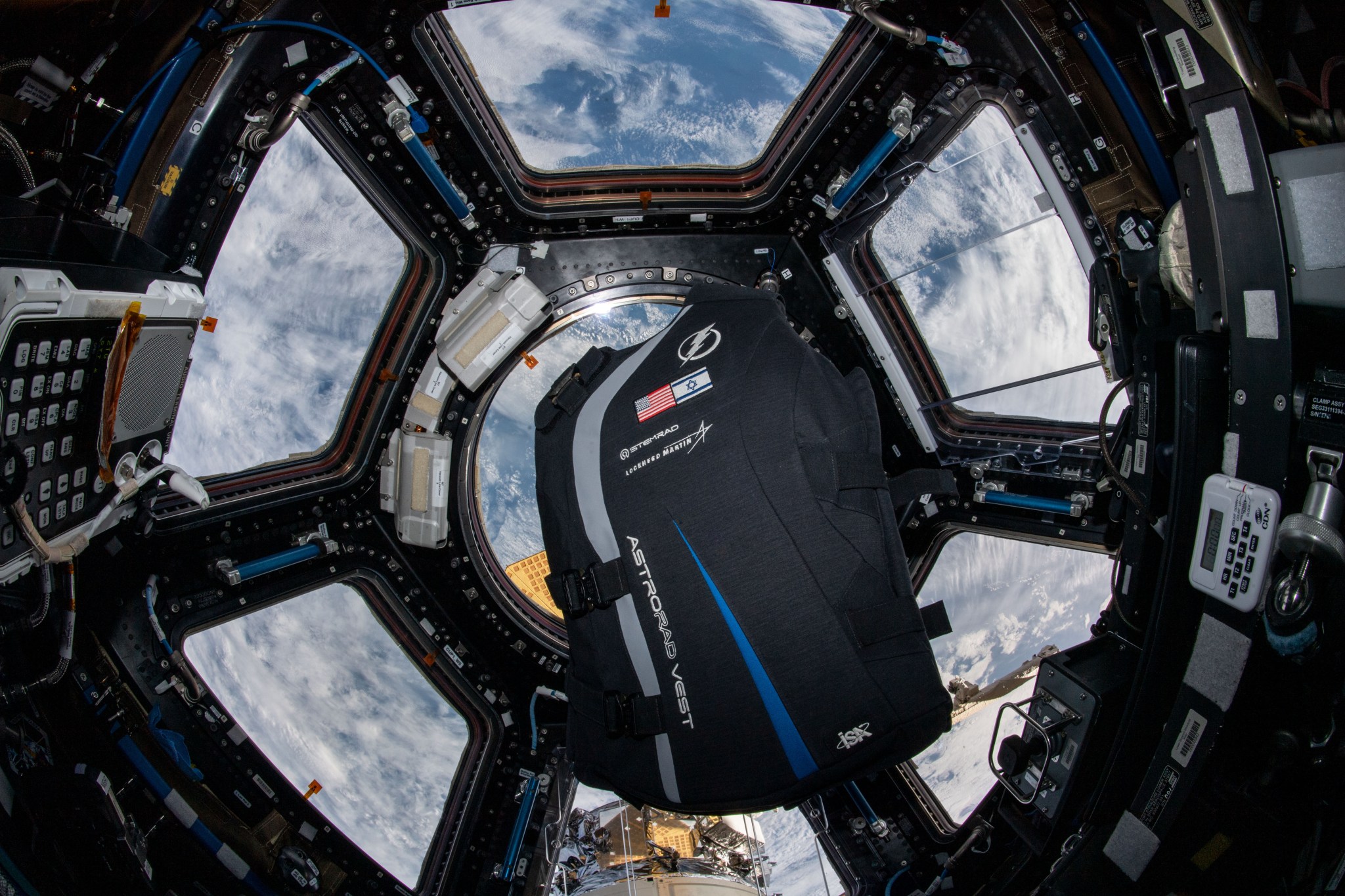
Station-tested radiation technology flown on Artemis I
The Orion spacecraft carried 5,600 passive and 34 active radiation detectors on its Artemis I uncrewed mission around the Moon in November 2022. Some of these devices previously were tested on the space station: HERA (Hybrid Electronic Radiation Assessor), which detects radiation events such as solar flares; the ESA (European Space Agency) Active Dosimeters, a wearable device collecting real-time data on individual radiation doses; and the AstroRad Vest, a garment to protect radiation-sensitive organs and tissues. In 2024, researchers released evaluation of data collected in 2022 by these tools that indicate the Orion spacecraft can protect astronauts on lunar missions from potentially hazardous radiation. The orbiting laboratory remains a valuable platform for testing technology for missions beyond Earth’s orbit.
Record participation in Fifth Robo-Pro Challenge
A record 661 teams and 2,788 applicants from thirteen countries, regions, and organizations participated in the fifth Kibo Robo-Pro Challenge, which wrapped its final round in September. This educational program from JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) has students solve various problems by programming free-flying Astrobee robots aboard the space station. Participants gain hands-on experience with space robot technology and software programming and interact with others from around the world.
Melissa Gaskill
International Space Station Research Communications Team|
Johnson Space Center